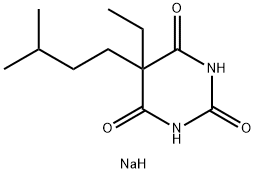
It is not common to see Amytal and other barbiturates prescribed anymore, and, in fact, many of them have been discontinued.
Benzodiazepines have replaced barbiturates in most markets and scenarios. They serve the same medical purpose as barbiturates but are found to be less addictive and habit-forming.